Abstract
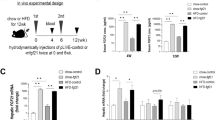
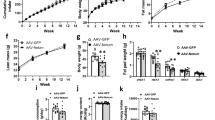
Angiopoietin-related growth factor (AGF), a member of the angiopoietin-like protein (Angptl) family, is secreted predominantly from the liver into the systemic circulation. Here, we show that most (>80%) of the AGF-deficient mice die at about embryonic day 13, whereas the surviving AGF-deficient mice develop marked obesity, lipid accumulation in skeletal muscle and liver, and insulin resistance accompanied by reduced energy expenditure relative to controls. In parallel, mice with targeted activation of AGF show leanness and increased insulin sensitivity resulting from increased energy expenditure. They are also protected from high-fat diet–induced obesity, insulin resistance and nonadipose tissue steatosis. Hepatic overexpression of AGF by adenoviral transduction, which leads to an approximately 2.5-fold increase in serum AGF concentrations, results in a significant (P < 0.01) body weight loss and increases insulin sensitivity in mice fed a high-fat diet. This study establishes AGF as a new hepatocyte-derived circulating factor that counteracts obesity and related insulin resistance.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Spiegelman, B.M. & Flier, J.S. Obesity and the regulation of energy balance. Cell 104, 531–543 (2001).
Matsuzawa, Y., Funahashi, T. & Nakamura, T. Molecular mechanism of metabolic syndrome X: Contribution of adipokines adipocyte-derived bioactive substances. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 832, 146–154 (1999).
Lowell, B.B., & Spiegelman, B.M. Towards a molecular understanding of adaptive thermogenesis. Nature 404, 652–660 (2000).
Levine, J.A., Eberhardt, N.L. & Jensen, M.D. Role of nonexercise activity thermogenesis in resistance to fat gain in human. Science 283, 212–214 (1999).
Gale, N.W., & Yancopoulos, G.D. Growth factors acting via endothelial cell-specific receptor tyrosine kinases: VEGFs, Angiopoietins, and ephrins in vascular development. Genes Dev. 13, 1055–1066 (1999).
Oike, Y. et al. Angiopoietin-related/like protein (ARPs/Angptls) regulate angiogenesis. Int. J. Hematol 80, 21–28 (2004).
Oike, Y. et al. Angiopoietin-related growth factor (AGF) promotes epidermal proliferation, remodeling and regeneration. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 100, 9494–9499 (2003).
Oike, Y. et al. Angiopoietin-related growth factor (AGF) promotes angiogenesis. Blood 103, 3760–3766 (2004).
Kim, I. et al. Molecular cloning, expression, and characterization of angiopoietin-related protein. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 26523–26528 (1999).
Camenisch, G. et al. ANGPTL3 stimulates endothelial cell adhesion and migration via Integrin αvβ3 and induces blood vessel formation in vivo. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 17281–17290 (2002).
Ito, Y. et al. Inhibition of angiogenesis and vascular leakiness by Angiopoietin-related protein 4. Cancer Res. 63, 6651–6657 (2003).
Yoon, J.C. et al. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma target gene encoding a novel angiopoietin-related protein associated with adipose differentiation. Mol. Cell Biol. 20, 5343–5349 (2000).
Kersten, S, et al. Characterization of the fasting-induced adipose factor FIAF, a novel peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor target gene. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 28488–28493 (2000).
Koishi, R, et al. Angptl3 regulates lipid metabolism in mice. Nat. Genet. 30, 151–157 (2002).
Inaba, T, et al. Angiopoietin-like protein 3 mediates hypertriglyceridemia induced by the liver X receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 21344–21351 (2003).
Evans, R.M., Barish, G.D. & Wang, Y.X. PPARs and the complex journey to obesity. Nat. Med. 10, 355–361 (2004).
Spiegelman, B.M. & Flier, J.S. Adipogenesis and obesity: Rounding out the big picture. Cell 87, 377–389 (1996).
Uysal, K.T., Wiesbrock, S.M., Marino, M.W. & Hotamisligil, G.S. Protection from obesity-induced insulin resistance in mice lacking TNF-α function. Nature 389, 610–614 (1997).
Peraldi, P., Xu, M. & Spiegelman, B.M. Thiazolidinediones block tumor necrosis factor-a-induced inhibitor of insulin signaling. J. Clin. Invest. 100, 1863–1869 (1997).
Yamauchi, T. et al. The fat-derived hormone adiponectin reverses insulin resistance associated with both lipoatrophy and obesity. Nat. Med. 7, 941–946 (2001).
Berg, A.H., Combs, T.P., Du, X., Brownlee, M. & Scherer, P.E. The adipocyte-secreted protein Acrp30 enhances hepatic insulin action. Nat. Med. 7, 647–653 (2001).
Shimomura, I., Hammer, R.E., Ikemoto, S., Brown, M.S. & Goldstein, J.L. Leptin reverses insulin resistance and diabetes mellitus in mice with congenital lipodystrophy. Nature 401, 73–76 (1999).
Friedman, J.M. Obesity in the new millennium. Nature 404, 632–634 (2000).
Lowell, B.B., et al. Development of obesity in transgenic mice after genetic ablation of brown adipose tissue. Nature 366, 740–742 (1993).
Zurlo, F., Larson, K., Bogardus, C. & Ravussin, E. Skeletal muscle metabolism is a major determinant of resting energy expenditure. J. Clin. Invest. 86, 1423–1427 (1990).
Kamei, Y. et al. PPARγ coactivator 1β/ERR ligand 1 is an ERR protein ligand, whose expression induces a high-energy expenditure and antagonizes obesity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 100, 12378–12383 (2003).
Niwa, H., Yamamura, K. & Miyazaki J. Efficient selection for high-expression transfectants with a novel eukaryotic vector. Gene 108, 193–200 (1991).
Sierra-Honigmann, M.R. et al. Biological action of leptin as an angiogenic factor. Science 281, 1683–1686 (1998).
Sarmiento, U., et al. Morphologic and molecular changes induced by recombinant human leptin in the white and brown adipose tissues of C57BL/6 mice. Lab. Invest. 77, 243–256 (1997).
Shimomura, I. et al. Insulin resistance and diabetes mellitus in transgenic mice expressing nuclear SREBP-1c in adipose tissue: model for congenital generalized lipodystrophy. Genes Dev. 12, 3182–3194 (1998).
Gavrilova, O. et al. Surgical implantation of adipose tissue reverses diabetes in lipoatrophic mice. J. Clin. Invest. 105, 271–278 (2000).
Moller, D.E. & Berger, J.P. Role of PPARs in the regulation of obesity-related insulin sensitivity and inflammation. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 27, S17–S21 (2003).
Wu, Z., et al. Mechanisms controlling mitochondrial biogenesis and respiration through the thermogenic coactivator PGC-1. Cell 98, 115–124 (1999).
Puigverger, P. et al. Cytokine stimulation of energy expenditure through p38 MAP kinase activation of PPARγ coactivator-1. Mol. Cell 8, 971–982 (2001).
Puigserver, P. & Spiegelman, B.M. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ coactivator 1α (PGC-1α): Transcriptional coactivator and metabolic regulator. Endocr. Rev. 24, 78–90 (2003).
Wang, Y.X. et al. Peroxisome-proliferator-activated receptor δ activates fat metabolism to prevent obesity. Cell 113, 159–70 (2003).
Tanaka, T. et al. Activation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor delta induces fatty acid beta-oxidation in skeletal muscle and attenuates metabolic syndrome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 100, 15924–15929 (2003).
Dressel, U. et al. The peroxisome proliferatior-activated receptor β/δ agonist, GW501516, regulates the expression of genes involved in lipid catabolism and energy uncoupling in skeletal muscle cells. Mol. Endocrinol. 17, 2477–2493 (2003).
Shulman, G.I., et al. Cellular mechanisms of insulin resistance. J. Clin. Invest. 106, 171–176 (2000).
Petersen, K.F. et al. Mitochondrial dysfunction in the elderly: Possible role in insulin resistance. Science 300, 1140–1142 (2003).
Barger, P.M., Browning, A.C., Garner, A.N. & Kelly, D.P. p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase activates peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α: a potential role in the cardiac metabolic stress response. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 44495–44501 (2001).
Acknowledgements
We thank K. Fukushima for her assistance with the experiments. This work was supported by Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research on Priority Areas from the Ministry of Education, Science and Culture of Japan, by the Yamanouchi Foundation for Research on Metabolic Disorders and by the Mochida Memorial Foundation for Medical and Pharmaceutical Research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The research concerned was performed under the Collaborative Research Agreement with Yamanouchi Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Fig. 1
Gene targeting of the AGF locus. (PDF 58 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 2
Generation of AGF-transgenic mice. (PDF 73 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 3
AGF-stimulated intracellular signaling in C2C12 myocytes. (PDF 70 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 4
Impaired blood flow perfusion in AGF−/− females. (PDF 33 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oike, Y., Akao, M., Yasunaga, K. et al. Angiopoietin-related growth factor antagonizes obesity and insulin resistance. Nat Med 11, 400–408 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/nm1214
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nm1214
This article is cited by
-
ANGPTL4 is a potential driver of HCV-induced peripheral insulin resistance
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and liver secretome
Archives of Pharmacal Research (2022)
-
Interplay between adipose tissue secreted proteins, eating behavior and obesity
European Journal of Nutrition (2022)
-
Senolytic vaccination improves normal and pathological age-related phenotypes and increases lifespan in progeroid mice
Nature Aging (2021)
-
Molecular cloning and characterization of angiopoietin-like protein-8 gene in pigs and its tissue-specific expression in different animals
Biologia (2021)